Professional Supplier of Laboratory Scientific Instruments
Professional Supplier of Laboratory Scientific Instruments
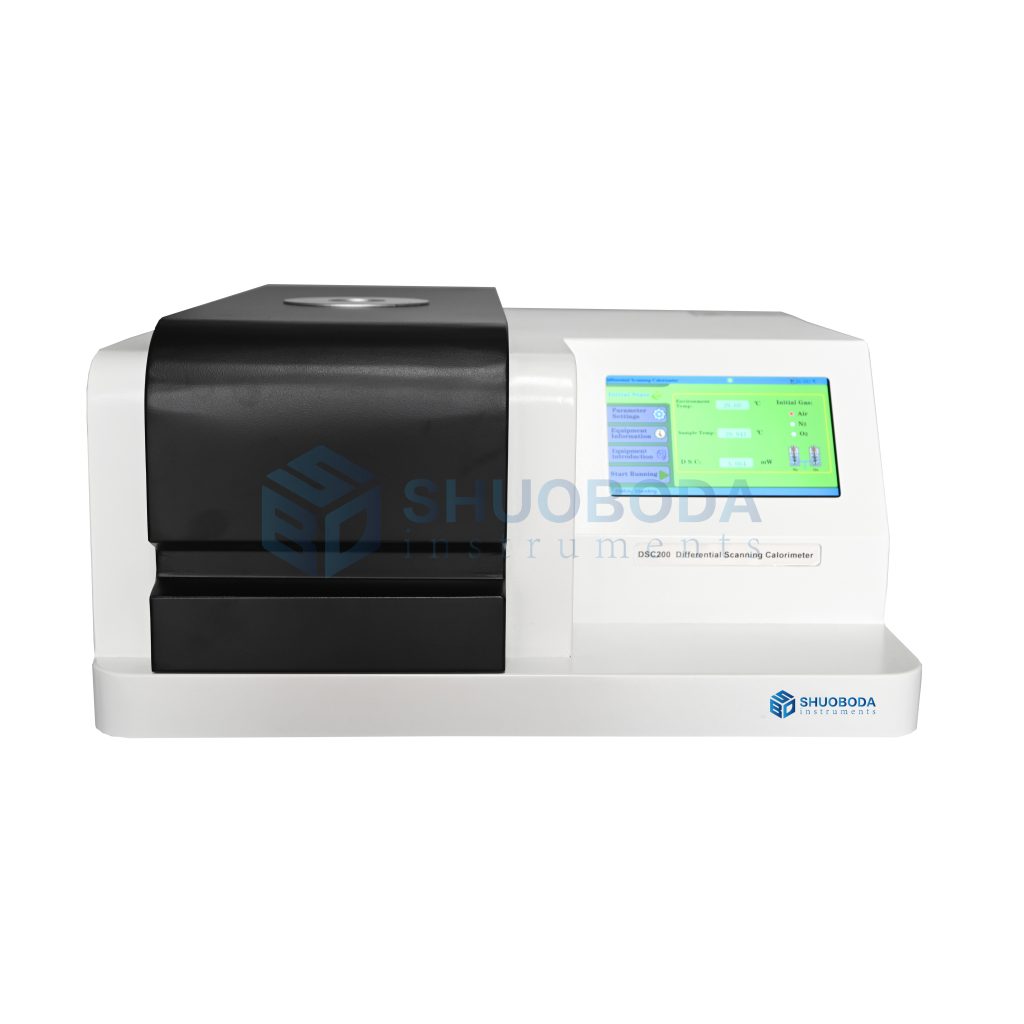
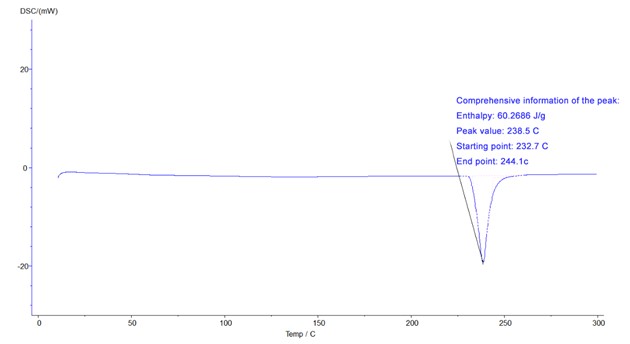
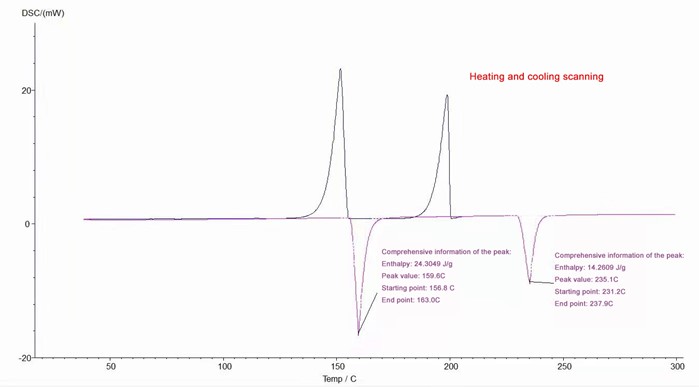
Differential scanning calorimeter can test glass transition temperature, phase transition temperature, melting point, enthalpy value, curing temperature, product stability, oxidation induction period, etc.

Differential Scanning Calorimeter DSC Operation Video
DSC-200A DSC differential scanning calorimeter is one of the most accurate DSC series products launched by the company. The sensor is made of imported material E-pair, which has high accuracy, high sensitivity and good repeatability. The signal acquisition circuit has shielding protection, strong anti-interference, and extremely high baseline stability and repeatability.
DSC-200A differential scanning calorimeter can be used to test glass transition temperature, phase transition temperature, melting point, enthalpy value, curing temperature, product stability, oxidation induction period, etc. It is competent in the research of pipes, polymers, chemicals, food, medical treatment and many other fields, and its products serve universities, enterprises, third-party measurement and quality inspection units, with a wide range of applications to meet the testing needs of various industries.


| MODEL | DSC-200A |
| Temperature range | 0~600℃ |
| Temperature resolution | 0.001℃ |
| Temperature fluctuation | ±0.001℃ |
| Temperature repeatability | ±0.01℃ |
| Heating rate | 0.1~80℃/min |
| The constant temperature time | Was programmed for 24h |
| Temperature control mode | Heating up, constant temperature, cooling (fully automatic program control) |
| DSC range | 0~±600mW |
| DSC, resolution | 0.01uW |
| DSC, sensitivity | 0.001mW |
| Working power supply | AC220V / 50Hz or customized |
| The atmosphere controls the gas | Nitrogen, oxygen (programmed / automatic switching) |
| Gas-flow rate | 0-300mL/min |
| Gas pressure | 0.2MPa |
| Display mode | 24bit color, 7-inch LCD touchscreen display |
| Data interface | Standard USB interface |
| Parameter standard | Equipped with a standard material (indium, tin), the user can correct the temperature by himself |
| Optional Cooling device | Air cooling device (optional semiconductor -40~550℃, liquid nitrogen refrigeration -150~550℃) |
| Thermocouple | with multiple sets of thermocouples, temperature of a group of measured samples,One group to measure furnace temperature,One group measures the internal ambient temperature |
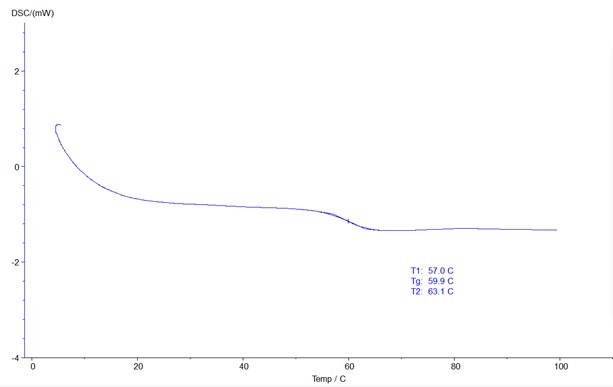
For amorphous polymers, when the polymer changes from a high elastic state to a glass state through cooling, or from a glass state to a high elastic state through heating, the process is called the glass transition, and the temperature at which the glass transition occurs is called the glass transition temperature. For crystalline polymers, the glass transition refers to the transition of the amorphous part from the high elastic state to the glass state (or the glass state to the high elastic state). Therefore, glass transition is a common phenomenon in polymers. However, the glass transition phenomenon is not limited to polymers, and some small molecular compounds also have glass transition.
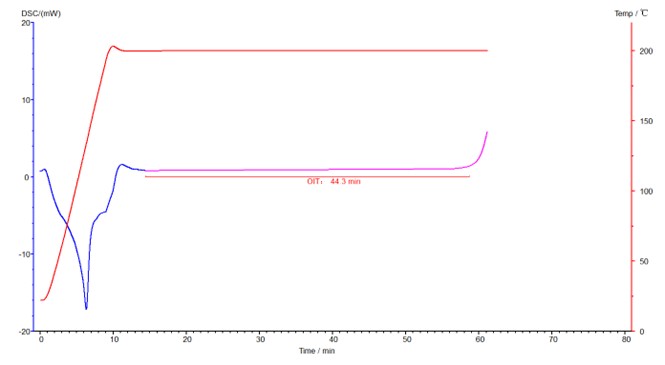
The oxidation induction time (OIT) was measured by DSC (differential scanning calorimeter). The sample is usually heated to the specified temperature and constant temperature under nitrogen atmosphere, and then switched to oxygen atmosphere. After a period of time, the material begins to oxidize and release heat. The released heat is detected by the sensor, and the induced oxidation time (OIT) is obtained through software analysis. The length of the oxidation induction time is a parameter of the oxidation decomposition resistance of the reaction material, which is still very meaningful. Usually, the parameter must be detected for buried plastic pipes.
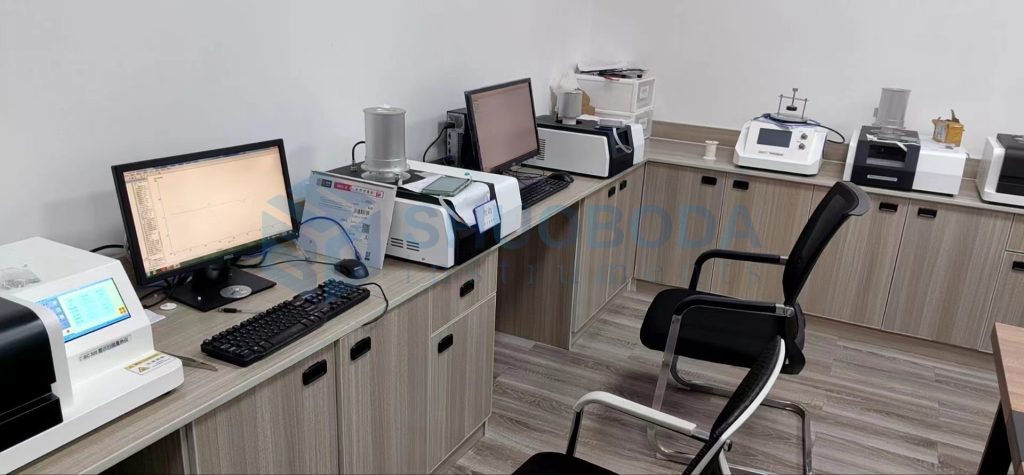
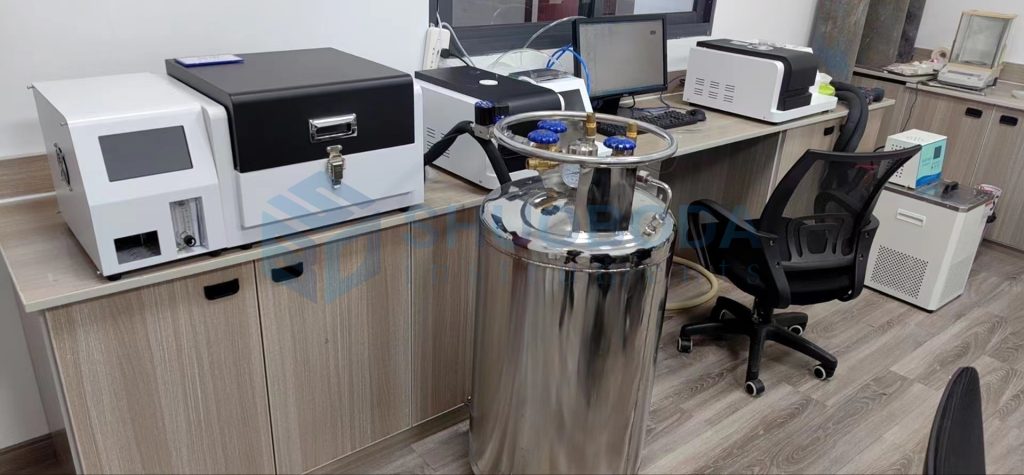
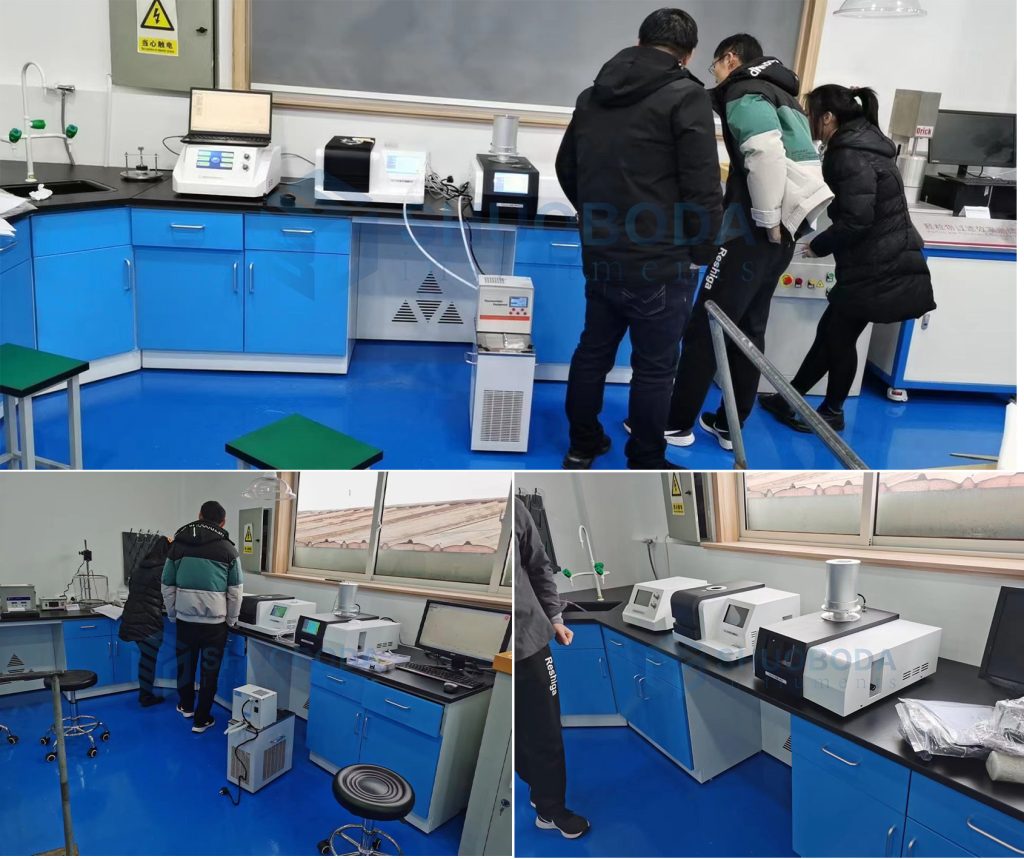








Experienced service team and strong production support team provide client worry-free order service.


If you are interested in any of our products or would like to discuss a customized order, Please feel free to contact us.
Contact Us